Changing Location of Workflow Container Images
We’ve noticed that common struggle from GridION and PromethION users of EPI2ME Labs
Nextflow workflows is that the default location in which Docker stores our workflow
container images is the somewhat small “root partition” of the devices. In this
post we will walk through how to change the location at which Docker stores these
data to the larger /data volume on the sequencing devices.
Users who have a Docker installation provided through installation of recent versions of MinKNOW should not follow these instructions. If in doubt contact support@nanoporetech.com.
Docker Configuration
The configuration of the Docker daemon, the process that is responsible for starting, running, managing, and ultimately killing containers is handled through a single JSON formatted configuration files. Common to other Linux systems this file is located at:
/etc/docker/daemon.json
on the GridION and PromethION sequencing platforms. To change the location where Docker (and hence Nextflow) stores the container images associated with workflows it is this file that we must edit.
Altering the Docker configuration and stopping and restarting the Docker daemon requires root access. The commands in this document are all run with
sudofor this reason.
The default directory where Docker keeps persistent data under Linux is:
/var/lib/docker
On GridION and PromethION sequencing devices, this location is stored on a somewhat small hard drive partition that was not intended for storage of large data. To change the location we need to edit the file noted above to tell Docker a more appropriate location to use for storage.
To start, open a terminal window and enter the command:
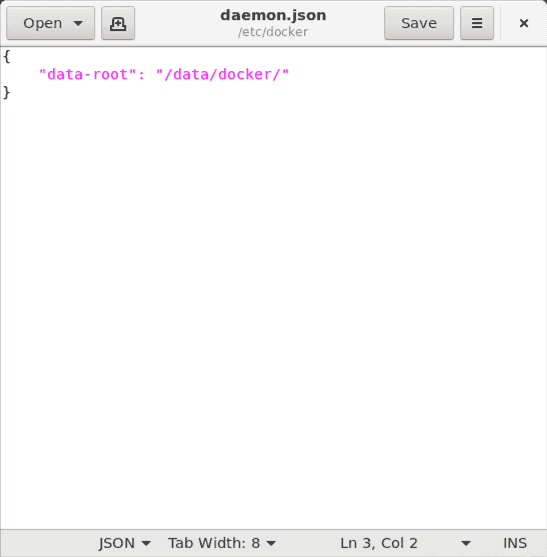
sudo gedit /etc/docker/daemon.json
This file should be empty, if it is not it is possible that your Docker installation has been preconfigured either by an installation of MinKNOW or by another user. Contact support@nanoporetech.com if the contents of this file are unfamiliar to you.
In the event that the file is empty, let us proceed to set the Docker storage location. Copy and paste the following into the gedit text editor:
{"data-root": "/data/docker/"}
and click the ‘Save’ button in gedit.
Close gedit and return to the terminal window. Enter the following command to restart the Docker daemon with the new settings applied:
sudo systemctl restart docker
The command may take a few seconds to run. To test the new settings let us run a Docker container and check that Docker uses the new storage location. Run a simple container with:
# first remove any existing imagedocker image rm ubuntu:latest# now download and run a fresh copy of the imagedocker run --rm ubuntu:latest echo Hello
The output of this command should be something like:
Unable to find image 'ubuntu:latest' locallylatest: Pulling from library/ubuntu7b1a6ab2e44d: Pull completeDigest: sha256:626ffe58f6e7566e00254b638eb7e0f3b11d4da9675088f4781a50ae288f3322Status: Downloaded newer image for ubuntu:latestHello
Running the command below should reveal content at the path specified:
sudo ls /data/docker/
If this is not the case we again recommend contacting support@nanoporetech.com for further assistance.
Summary
This guide has walked through configuring the “data-root” configuration item of the Docker daemon, and restarting the daemon for these changes to take effect. For more information on configuring Docker on Linux systems see the official documentation.